-
Study
-
Quick Links
- Open Days & Events
- Real-World Learning
- Unlock Your Potential
- Tuition Fees, Funding & Scholarships
- Real World Learning
-
Undergraduate
- Application Guides
- UCAS Exhibitions
- Extended Degrees
- School & College Outreach
- Information for Parents
-
Postgraduate
- Application Guide
- Postgraduate Research Degrees
- Flexible Learning
- Change Direction
- Register your Interest
-
Student Life
- Students' Union
- The Hub - Student Blog
- Accommodation
- Northumbria Sport
- Support for Students
-
Learning Experience
- Real-World Learning
- Research-enriched learning
- Graduate Futures
- The Business Clinic
- Study Abroad
-
-
International
International
Northumbria’s global footprint touches every continent across the world, through our global partnerships across 17 institutions in 10 countries, to our 277,000 strong alumni community and 150 recruitment partners – we prepare our students for the challenges of tomorrow. Discover more about how to join Northumbria’s global family or our partnerships.
View our Global Footprint-
International Students
- Information for International Students
- Northumbria and your Country
- International Student Events
- Application Guide
- Entry Requirements and Education Country Agents
- Global Offices and Regional Teams
- English Requirements
- English Language Centre
- International student support
- Cost of Living
-
International Fees and Funding
- International Undergraduate Fees
- International Undergraduate Funding
- International Masters Fees
- International Masters Funding
- International Postgraduate Research Fees
- International Postgraduate Research Funding
- Useful Financial Information
-
International Partners
- Agent and Representatives Network
- Global Partnerships
- Global Community
-
International Mobility
- Study Abroad
- Information for Incoming Exchange Students
-
-
Business
Business
The world is changing faster than ever before. The future is there to be won by organisations who find ways to turn today's possibilities into tomorrows competitive edge. In a connected world, collaboration can be the key to success.
More on our Business Services-
Business Quick Links
- Contact Us
- Business Events
- Research and Consultancy
- Education and Training
- Workforce Development Courses
- Join our mailing list
-
Education and Training
- Higher and Degree Apprenticeships
- Continuing Professional Development
- Apprenticeship Fees & Funding
- Apprenticeship FAQs
- How to Develop an Apprentice
- Apprenticeship Vacancies
- Enquire Now
-
Research and Consultancy
- Space
- Energy
- AI Futures
- CHASE: Centre for Health and Social Equity
- NESST
-
-
Research
Research
Northumbria is a research-rich, business-focused, professional university with a global reputation for academic quality. We conduct ground-breaking research that is responsive to the science & technology, health & well being, economic and social and arts & cultural needs for the communities
Discover more about our Research-
Quick Links
- Research Peaks of Excellence
- Academic Departments
- Research Staff
- Postgraduate Research Studentships
- Research Events
-
Research at Northumbria
- Interdisciplinary Research Themes
- Research Impact
- REF
- Partners and Collaborators
-
Support for Researchers
- Research and Innovation Services Staff
- Researcher Development and Training
- Ethics, Integrity, and Trusted Research
- University Library
- Vice Chancellors Fellows
-
Research Degrees
- Postgraduate Research Overview
- Doctoral Training Partnerships and Centres
- Academic Departments
-
Research Culture
- Research Culture
- Research Culture Action Plan
- Concordats and Commitments
-
-
About Us
-
About Northumbria
- Our Strategy
- Our Staff
- Our Schools
- Place and Partnerships
- Leadership & Governance
- University Services
- Northumbria History
- Contact us
- Online Shop
-
-
Alumni
Alumni
Northumbria University is renowned for the calibre of its business-ready graduates. Our alumni network has over 253,000 graduates based in 178 countries worldwide in a range of sectors, our alumni are making a real impact on the world.
Our Alumni - Work For Us
A forensic scientist from Northumbria University was part of a team that revealed members of a mysterious archaic human species buried their dead long before the earliest evidence of burials by modern humans.
Dr Patrick Randolph-Quinney is Associate Professor of Forensic Science at Northumbria and specialises in taphonomy and thanatology – the science of death and the multiple processes that affect a body from decomposition, through to skeletonization, then recovery.
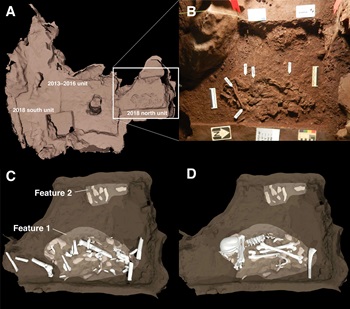
In a project funded by the National Geographic Society, Dr Randolph-Quinney was one of a team of experts that unearthed new evidence in the Rising Star cave system in South Africa suggesting ‘Homo naledi’ – an extinct human cousin – buried their dead. This symbolic behaviour has been previously associated only with modern humans and Neanderthals.
In their search to understand human origins, the team of explorers identified depressions deep in the chambers of the Rising Star cave system. Bodies of Homo naledi adults and several children, estimated to be younger than 13 years of age, were deposited in foetal positions within pits, which suggests intentional burial of the dead.
These findings – which have been covered in National Geographic – could be some of the earliest examples of burial practices by a small-brained human relative, thus altering our understanding of human evolution.
The Homo naledi fossils have been dated to around 226,000 – 335,000 years old. This predates the earliest known Homo sapiens’ burials by at least 100,000 years, making the Rising Star burials the most ancient in the human evolutionary record.
Fossils belonging to Homo naledi were first discovered in the Rising Star cave system in South Africa during excavations in 2013. The cave system is part of South Africa’s Cradle of Humankind, a UNESCO World Heritage Site encompassing an area where scientists have found fossils of multiple ancient human species, unlocking new evidence about how our ancient human ancestors lived.
Dr Randolph-Quinney has worked extensively in funerary and mortuary archaeology, recovering human and animal remains from deep prehistory through to the recent past. As a forensic scientist he has extensive casework experience in both forensic anthropology and archaeology in the UK and sub‐Saharan Africa, including recovery of bodies from homicides, fatal fires, and human rights abuses.
He has used his experience from funerary archaeology and forensic casework, together with experimental studies of how human bodies decompose, and methods of 3D imaging and spatial analysis, to help understand the site formation processes and burials of Homo naledi within the Rising Star cave system.
“Forensic science has helped the research at Rising Star since the excavation of the first fossils from the site back in 2013,” he said. “I have used a branch of forensic science called forensic taphonomy to understand the processes that affected the bodies of Homo naledi after they died.
“Forensic taphonomy uses data from experiments conducted at forensic research facilities – so-called body farms – where decomposition of humans and other animals can be studied in a variety of settings, as well as forensic casework to understand what happens to a body after death.
“Forensic scientists try to understand the many processes that can affect a body after death – the pattern of decomposition, how long it takes, which parts of the body separate and when, and the effects of soil, water and scavengers on the skeleton. We use this accumulated forensic data to determine that bodies of Homo naledi were deliberately placed in graves within the cave, and covered up with cave sediments, a process known as interment.”

According to Dr Randolph-Quinney we have a few lines of evidence that Homo naledi buried their dead. Firstly, there is evidence of a grave cut, which is a hole that Homo naledi deliberately made in the cave floor to contain the dead bodies. Secondly, the pattern of bones within the graves is consistent with a body that is flexed or curled-up. Dr Randolph-Quinney could determine the body was flexed using x-ray imaging, which allowed him to see inside the sediment of the grave. He states that the relationship between the bones is what a forensic scientist would expect to see if a body decomposed in a flexed position.
And while Dr Randolph-Quinney acknowledges that we don’t know exactly why Homo naledi buried their dead, we do know that humans and many other animals understand that death is important.
“Humans have a huge range of funerary customs including burial in the ground, cremation, leaving a body in the open air and mummification,” said Dr Randolph-Quinney. “We know that humans experience grief and sadness when someone they know dies, and these emotions seem to be experienced by non-humans such as chimpanzees, elephants, and crows. These animals don’t bury their dead, but they do have rituals and behaviours that seem to indicate they feel grief and understand that the dead aren’t coming back to life. It’s likely Homo naledi shared these emotions too, and burial of their dead was a way of recognising the importance and finality of death.”
These and other findings are detailed in three studies that have been accepted for publication in the journal eLife, and preprinted in BioRxiv: Evidence for deliberate burial of the dead by Homo naledi; 241,000 to 335,000 years old rock engravings made by Homo naledi in the Rising Star Cave system, South Africa and Burials and engravings in a small brained hominin, Homo naledi, from the late Pleistocene: contexts and evolutionary implications.
The Forensic Science Research Group (FSRG) at Northumbria comprises a highly skilled group of scientists and ex-practitioners in forensic science. Members of the group are working in a range of subjects from analytical chemistry, human biology, microbiology, and statistical modelling to the application of forensic policy and the law. They have published widely in forensic science and other applied subject areas and have contributed to casework in the investigation of major crimes, including homicide, serious sexual assault and crimes against humanity. Northumbria University has been ranked fourth in the UK for Forensic Science in the Complete University Guide 2024.News
- Telescope reveals surprising secrets in Jupiter's northern lights
- Working-class roots drive North East graduate’s AI healthcare revolution
- National Fellowship honours Northumbria nursing leader
- Venice Biennale Fellowship
- First cohort of Civil Engineering Degree Apprentices graduate from Northumbria
- Northumbria expands results day support for students
- Northumbria academic recognised in the British Forces in Business Awards 2025
- £1.2m grant extends research into the benefits of breast milk for premature babies
- Northumbria graduate entrepreneur takes the AI industry by storm
- Study identifies attitudes towards personal data processing for national security
- Lifetime Brands brings student design concept to life
- New study reveals Arabia’s ‘green past’ over the last 8 million years
- How evaluation can reform health and social care services
- Researchers embark on a project to further explore the experiences of children from military families
- Northumbria University's pioneering event series returns with insights on experiential and simulated learning
- Support for doctoral students to explore the experiences of women who have been in prison
- Funding boost to transform breastfeeding education and practice
- A new brand of coffee culture takes hold in the North East
- BBRSC awards £6m of funding for North East Bioscience Doctoral Students
- £3m funding to evaluate health and social care improvements
- Balfour Beatty apprentices graduate from Northumbria University
- Long COVID research team wins global award
- Northumbria researchers lead discussions at NIHR event on multiple and complex needs
- Healthcare training facility opens to support delivery of new T-level course
- Young people praise Northumbria University for delivery of HAF Plus pilot
- Nursing academics co-produce new play with Alphabetti Theatre
- Research project to explore the experiences of young people from military families
- Academy of Social Sciences welcomes two Northumbria Professors to its Fellowship
- Northumbria University set to host the Royal College of Nursings International Nursing Research Conference 2024
- 2.5m Award Funds Project To Encourage More People Into Health Research Careers
- Advice available for students ahead of A-level results day
- Teaching excellence recognised with two national awards
- Northumbria law student crowned first Apprentice of the Year for the region
- Northumbria University launches summer activities to support delivery of Holiday Activities and Food programme
- UK health leader receives honorary degree from Northumbria University
- Use of AI in diabetes education achieves national recognition
- Research animation explores first-hand experiences of receiving online support for eating disorders
- Careers event supports graduate employment opportunities
- Northumbria University announces £50m space skills, research and development centre set to transform the UK space industry
- The American Academy of Nursing honours Northumbria Professor with fellowship
- New report calls for more support for schools to improve health and wellbeing in children and young people
- AI experts explore the ethical use of video technology to support patients at risk of falls
- British Council Fellows selected from Northumbria University for Venice Biennale
- Prestigious nomination for Northumbria cyber security students
- Aspiring Architect wins prestigious industry awards
- Lottery funding announced to support mental health through creative education
- Early intervention can reduce food insecurity among military veterans
- Researching ethical review to support Responsible AI in Policing
- Northumbria named Best Design School at showcase New York Show
- North East universities working together
- Polar ice sheet melting records have toppled during the past decade
- Beyond Sustainability
- Brewing success: research reveals pandemic key learnings for future growth in craft beer industry
- City's universities among UK best
- Famous faces prepare to take to the stage to bring a research-based performance to life
- Insights into British and other immigrant sailors in the US Navy
- International appointment for law academic
- Lockdown hobby inspires award-winning business launch for Northumbria student
- Lasting tribute to Newcastle’s original feminist
- Outstanding service of Northumbria Professor recognised with international award
- Northumbria academics support teenagers to take the lead in wellbeing research
- Northumbria University becomes UK's first home of world-leading spectrometer
- Northumbria's Vice-Chancellor and Chief Executive to step down
- Out of this world experience for budding space scientists
- Northumbria engineering graduate named as one of the top 50 women in the industry
- Northumbria University signs up to sustainable fashion pledge
- Northumbria demonstrates commitment to mental health by joining Mental Health Charter Programme
- Virtual reality tool that helps people to assess household carbon emissions to go on display at COP26
- EXPERT COMMENT: Why thieves using e-scooters are targeting farms to steal £3,000 quad bikes, and what farmers can do to prevent it
- Exhibition of lecturer’s woodwork will help visitors reimagine Roman life along Hadrian’s Wall
- Students reimagine food economy at international Biodesign Challenge Summit
- Northumbria storms Blackboard Catalyst Awards
- Breaking news: Northumbria’s Spring/Summer Newspaper is here!
- UK’s first ever nursing degree apprentices graduate and join the frontline
- Massive decrease in fruit and vegetable intake reported by children receiving free school meals following lockdown
- Northumbria awards honorary degrees at University’s latest congregations
Latest News and Features

Recognition for researcher dedicated to tackling food insecurity in the UK
A Northumbria University academic who has played a key role in bringing breakfast clubs and…

University partnership brings space research to life for school pupils
A North East school has partnered with solar and space physics experts from Northumbria University…
.png?modified=20250916102106)
Telescope reveals surprising secrets in Jupiter's northern lights
An international team of scientists, led by a PhD researcher from Northumbria University, has…

Northumbria Film graduates receive Royal Television Society honours
Two Northumbria University Film graduates have won Royal Television Society (RTS) Student Awards…

Scientists reveal the best and worst-case scenarios for a warming Antarctica
A new analysis of decades of research on the Antarctic Peninsula, involving experts from Northumbria…

PhD student maps mysterious upper atmosphere of Uranus for the first time
A Northumbria University PhD student has led an international team of astronomers in creating…

Developing technology to help empower young innovators across the globe
Northumbria University researchers have joined forces with the International Federation of…

Working-class roots drive North East graduate’s AI healthcare revolution
A Northumbria University graduate has developed groundbreaking AI technology that could save…
Upcoming events

Launch of the Northern Interprofessional Education Strategy
Northumbria University
-
